what is diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology Ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka diabetes ucalgary calgaryguide physiology pathogenesis renal mellitus acidosis grepmed cetoacidosis metabolic clinical pharmacology enfermería complication
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that requires immediate medical attention. It occurs when the body’s cells do not receive enough glucose (sugar) for energy and instead start breaking down fat for fuel. This process produces ketones, which are acidic and can build up in the blood, leading to a condition called ketoacidosis.
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 The pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis involves various complex mechanisms. The image provided gives a clear visual representationof the process involved in DKA. It is important to note that this image is for illustrative purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
The pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis involves various complex mechanisms. The image provided gives a clear visual representationof the process involved in DKA. It is important to note that this image is for illustrative purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
When there is a lack of insulin or an insufficiency of its action, glucose cannot enter the cells, resulting in hyperglycemia. To compensate for this, the body starts breaking down fat into fatty acids, which are then converted into ketones in the liver. The accumulation of ketones leads to metabolic acidosis as they lower the blood pH.
Metabolic acidosis is a condition characterized by an imbalance in the body’s acid-base levels, with a decrease in bicarbonate levels and increased acidity in the blood. This leads to a range of symptoms including frequent urination, increased thirst, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fruity-scented breath.
The Importance of Timely Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a medical emergency that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as cerebral edema, which is the swelling of the brain. It can also result in hypokalemia, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.
The management of DKA involves several steps. Firstly, fluid and electrolyte replacement plays a critical role in correcting dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Intravenous fluids are administered to restore the body’s fluid balance and correct any electrolyte abnormalities.
In addition to fluid replacement, insulin therapy is administered to lower blood glucose levels and halt further ketone production. This is usually done through continuous intravenous insulin infusion, closely monitored by healthcare professionals.
 It is important to note that while this animation provides a simplified representation of the pathophysiology of DKA, the actual process is much more complex. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
It is important to note that while this animation provides a simplified representation of the pathophysiology of DKA, the actual process is much more complex. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Prevention and Future Considerations
Prevention plays a crucial role in avoiding the onset of Diabetic Ketoacidosis. This can be achieved through regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, ensuring compliance with insulin or other diabetes medications, and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs of infection or illness.
As technology advances, there is ongoing research into the development of more accurate glucose monitoring devices and improved insulin delivery methods. Continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps have shown promise in improving diabetes management and reducing the risk of complications such as DKA.
In conclusion, Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a serious complication that can occur in individuals with diabetes. Understanding its pathophysiology and recognizing the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment is crucial for managing this potentially life-threatening condition. By following proper preventive measures and utilizing advancements in diabetes care, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall quality of life and minimize the risk of complications like DKA.
If you are looking for Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Images about Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube like Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis | McMaster, Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube and also Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube. Here it is:
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube
 tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk walgreens a1c accuracy test glucose blood ph
tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk walgreens a1c accuracy test glucose blood ph
Pathogenesis And Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | McMaster
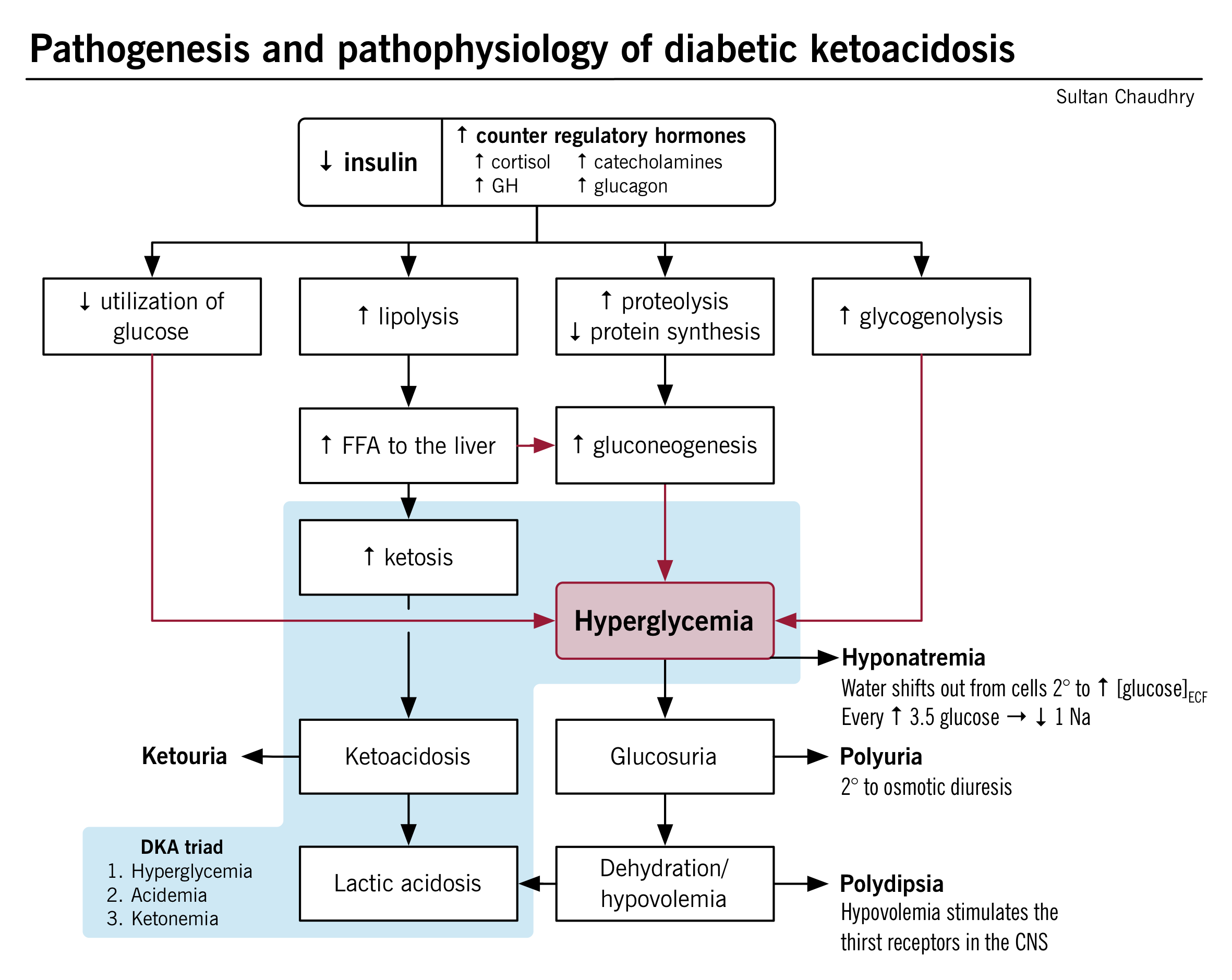 www.pathophys.orgketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology dka hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar pathogenesis emergencies hhs flowchart pathophys metabolic diabetes hyponatremia insulin acidosis syndrome mcmaster
www.pathophys.orgketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology dka hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar pathogenesis emergencies hhs flowchart pathophys metabolic diabetes hyponatremia insulin acidosis syndrome mcmaster
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Calgary Guide | Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 www.pinterest.comketoacidosis pathophysiology dka diabetes ucalgary calgaryguide physiology pathogenesis renal mellitus acidosis grepmed cetoacidosis metabolic clinical pharmacology enfermería complication
www.pinterest.comketoacidosis pathophysiology dka diabetes ucalgary calgaryguide physiology pathogenesis renal mellitus acidosis grepmed cetoacidosis metabolic clinical pharmacology enfermería complication
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Management (DKA) : Causes, Treatment, Prevention
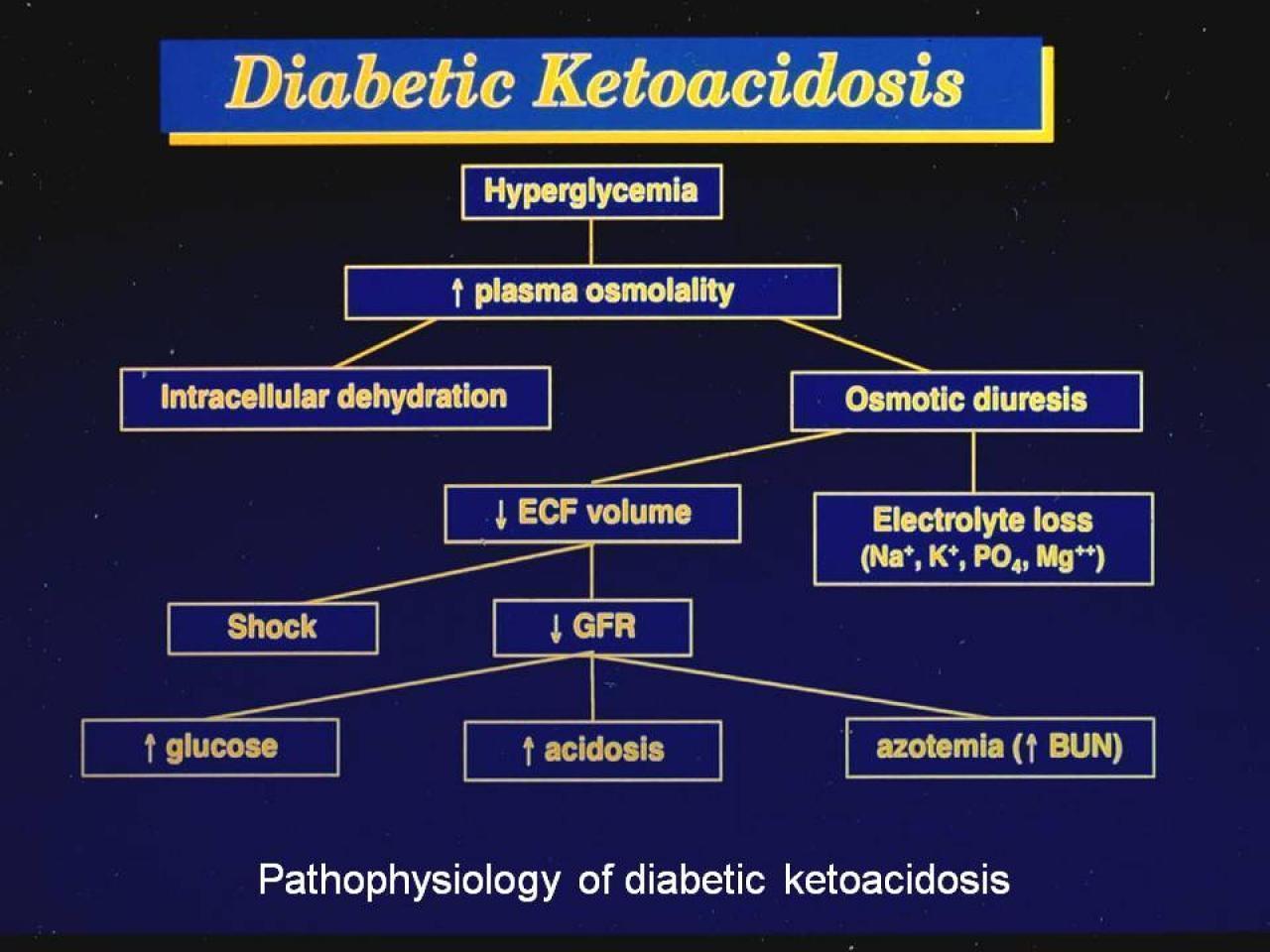 www.breathewellbeing.inketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology step1 medbullets endocrine insulin deficiency glucose pathophysiological
www.breathewellbeing.inketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology step1 medbullets endocrine insulin deficiency glucose pathophysiological
Medicowesome: Pathophysiology: Diabetic Ketoacidosis
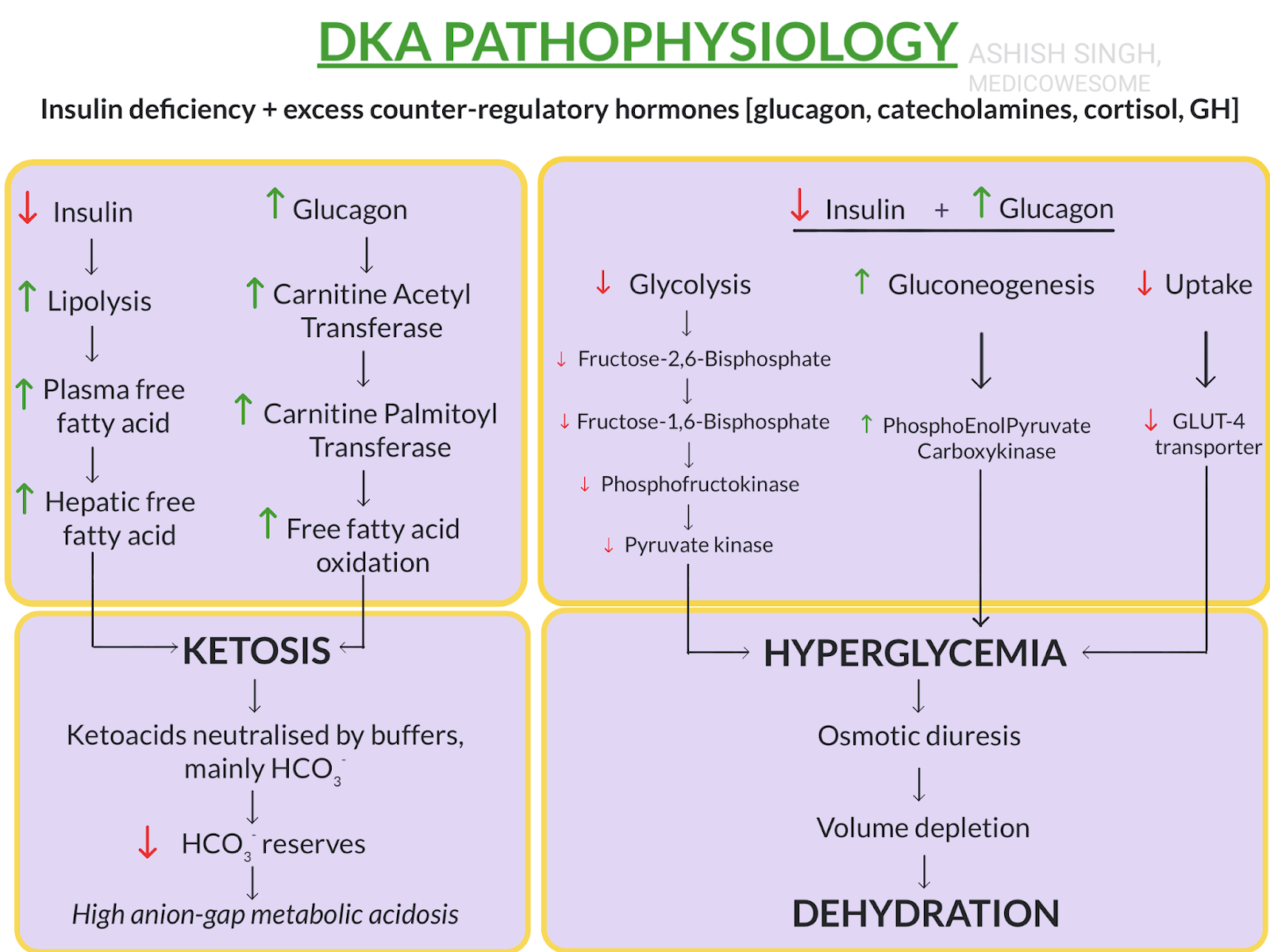 www.medicowesome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic dka summary happens
www.medicowesome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic dka summary happens
Ketoacidosis diabetic pathophysiology dka hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar pathogenesis emergencies hhs flowchart pathophys metabolic diabetes hyponatremia insulin acidosis syndrome mcmaster. Ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka diabetes ucalgary calgaryguide physiology pathogenesis renal mellitus acidosis grepmed cetoacidosis metabolic clinical pharmacology enfermería complication. Diabetic ketoacidosis management (dka) : causes, treatment, prevention